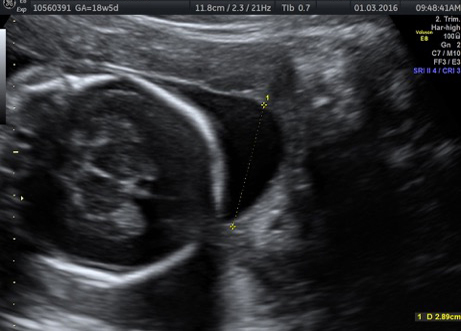
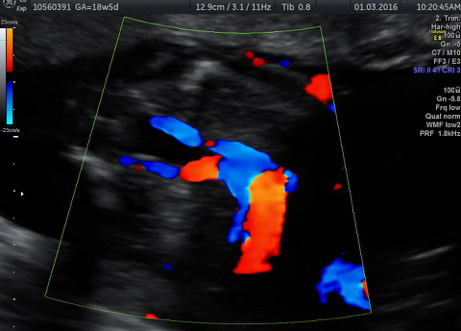
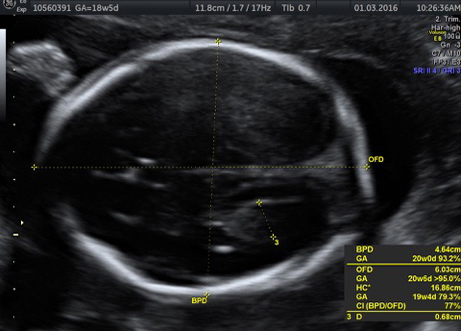
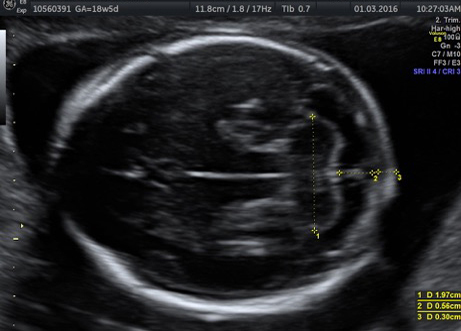
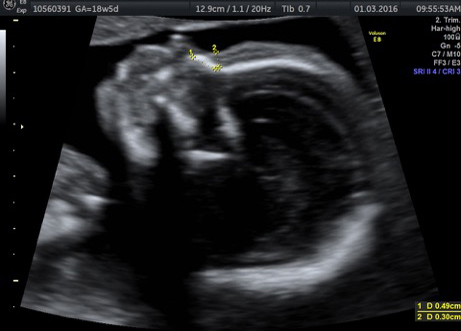
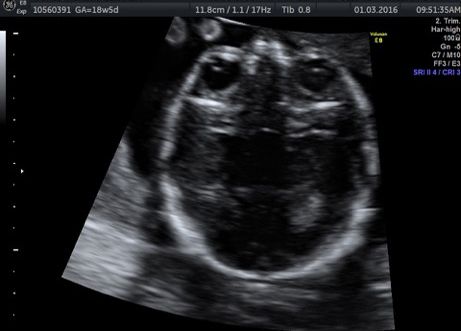
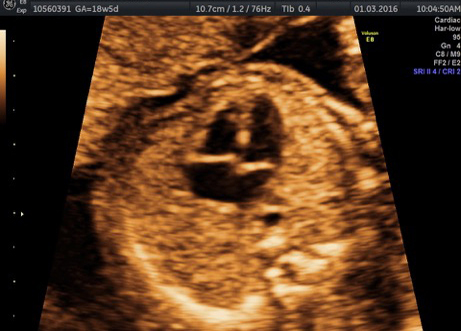
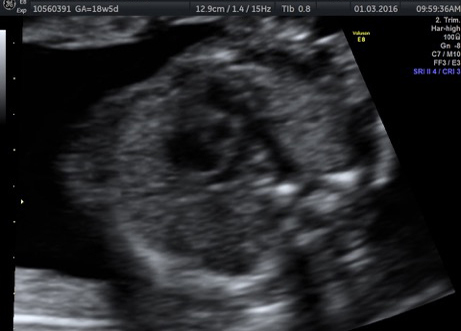
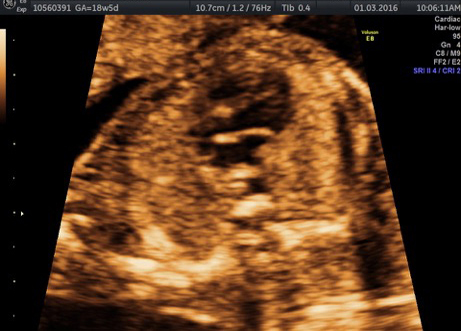
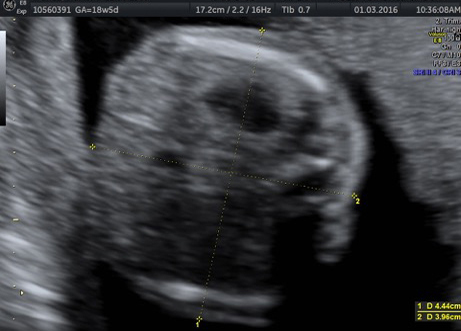
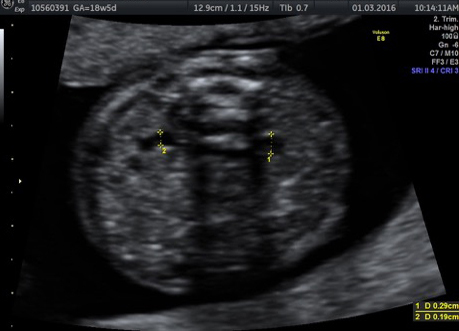
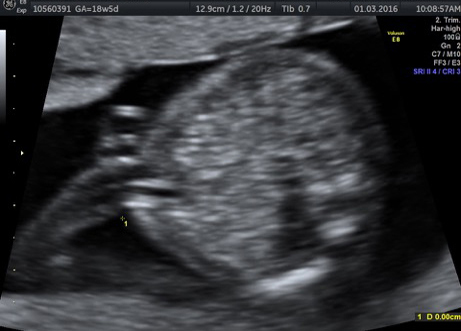
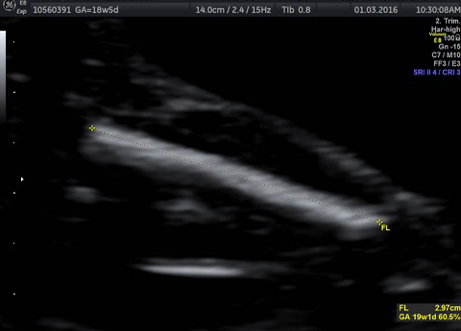
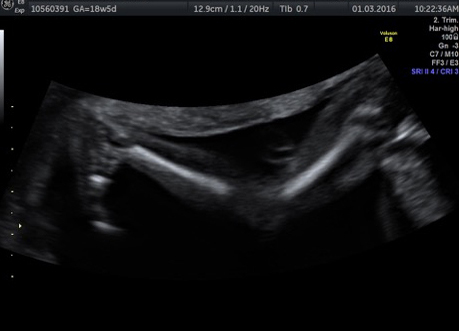
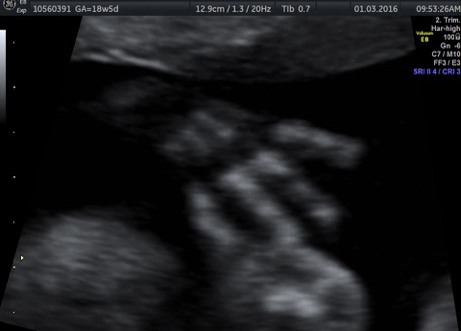
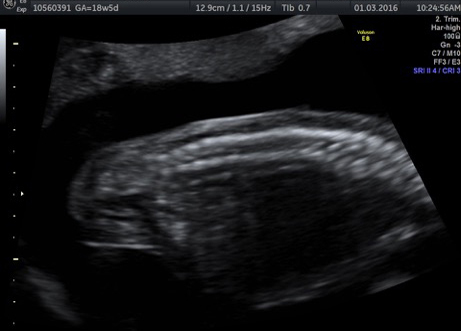
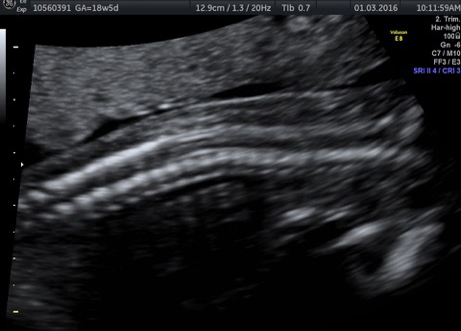
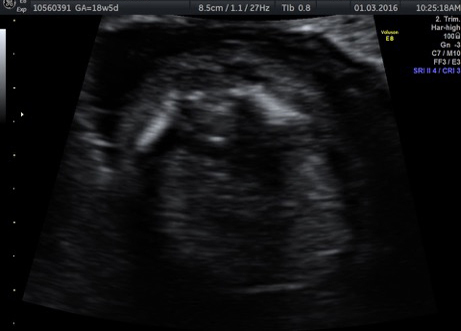
Genetic Sonogram or the risk reassessment scan is generally performed when the Down syndrome risk has increased on an earlier biochemical screening test.
In this an ultrasound is performed looking for specific ultrasound features or soft markers suggestive of T21 such as nuchal fold, nasal bone, mild ventriculomegaly, aberrant right subclavian artery.
Specific features are checked which either increase or decrease the risk of Down syndrome.
At the end of the scan a new probability risk for Down syndrome is given. The genetic sonogram is only 56% efficient at detecting Down syndrome at a false positive ration of 3%.