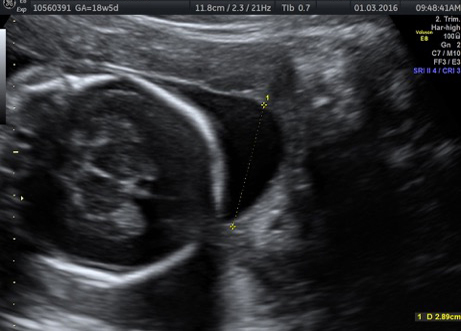
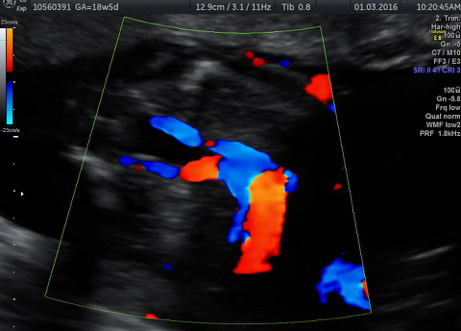
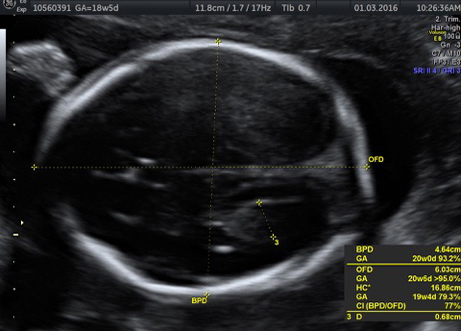
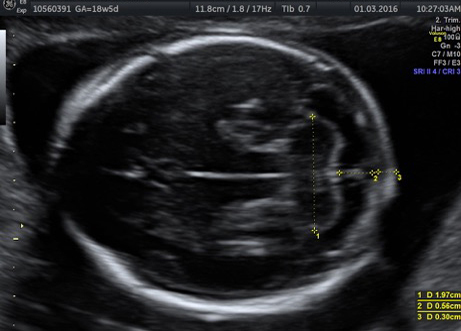
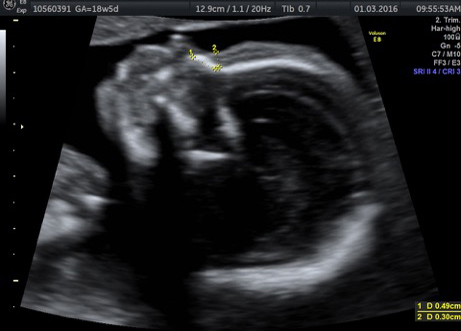
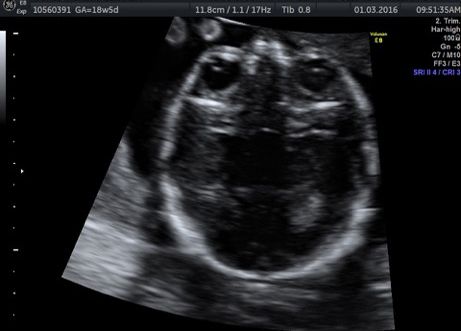
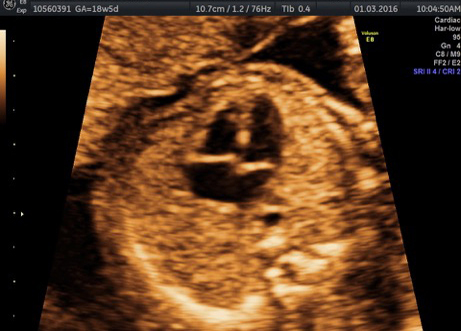
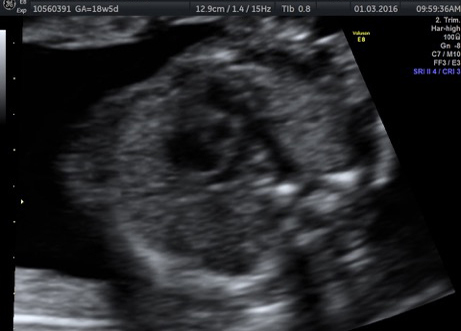
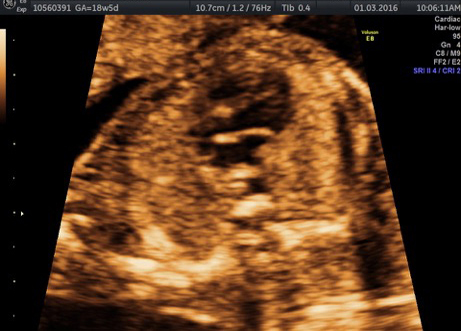
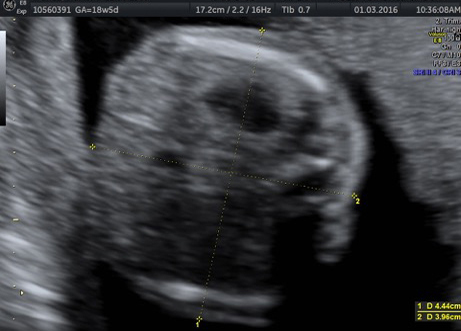
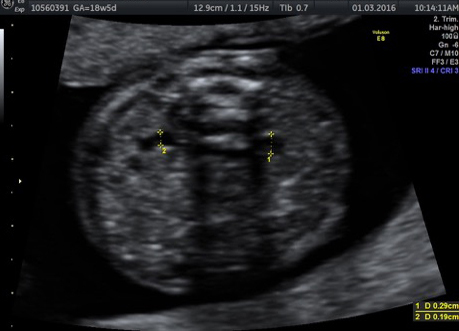
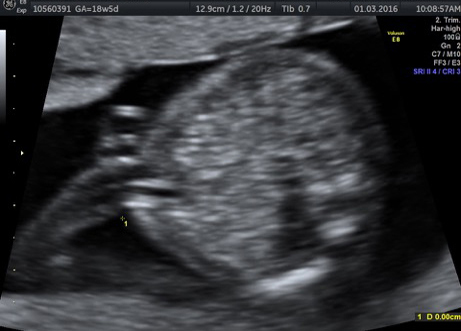
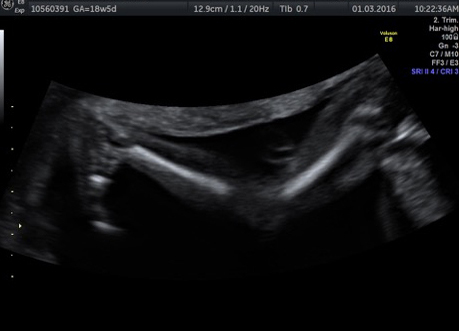
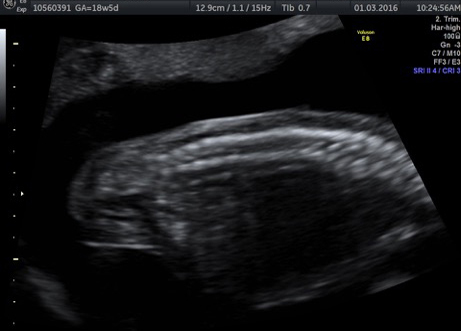
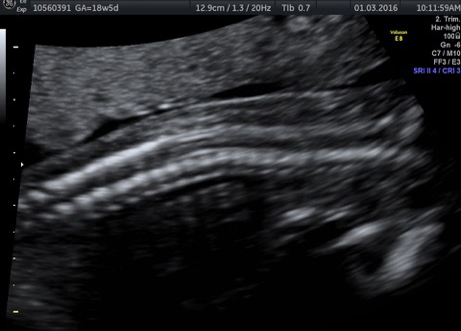
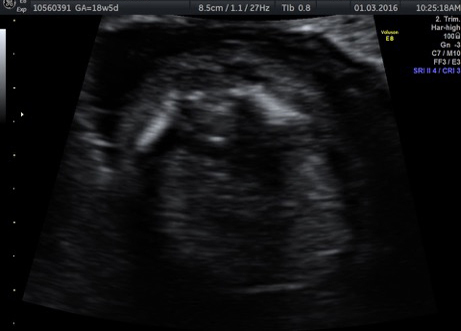
Fetal chylothorax or hydrothorax is a condition in which fluid accumulates in the fetal chest, in the space between the lungs and the chest wall (known as the pleural space). This fluid may also be referred to as “pleural effusion.” Fetal hydrothorax usually develops when there are leaky or obstructed veins or lymphatic channels. Occasionally, the fluid leakage may result from a mass (such as a lung mass), infection or chromosome problem, but in many instances no specific cause for the leaky fluid may be found. In some instances, the amount of fluid may be small. Occasionally, the amount of fluid is large, which may lead to pressure on the surrounding heart and lungs. In extreme cases, the fluid pushes the heart and other nearby structures to the other side of the chest, which can lead to decreased blood return and fetal heart failure, referred to as fetal “hydrops.” In such cases, drainage of the fluid, either with aspiration or placement of a drainage tube called thoracoamniotic shunt, will be to benefit to the health of the growing fetus.
The evaluation of pregnancies complicated by fetal hydrothorax includes a thorough fetal ultrasound and fetal echocardiogram, an ultrasound study of the fetus’ heart. These studies will evaluate the amount of fluid seen and try to determine whether there are ill-effects from this fluid. Your doctors will review these findings with you and discuss the treatment options for your individual case.