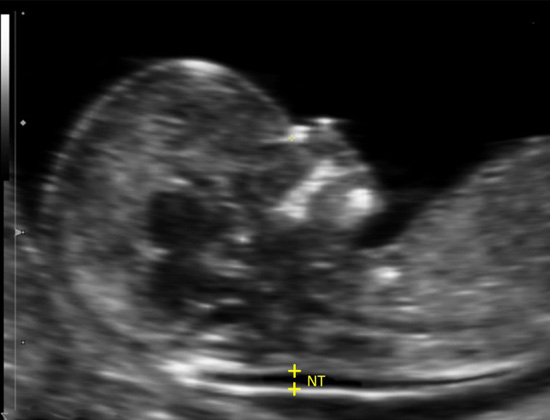
During pregnancy, some of the DNA from the baby crosses into mom’s bloodstream. DNA is organized in structures known as chromosomes, which carry the baby’s genetic information. There are several NIPT companies available in the market. As most of the companies are not from India, we allow the patients to decide which company their blood will be sent to, providing that company provides fetal fraction.
Most people have 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 — two copies of each set. The NIPT test is highly effective in determining if there is only one chromosome where there should be a pair, or if there is an extra chromosome, especially for the chromosomes that are responsible for Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome and certain sex chromosome trisomies. Panorama can also identify if there are three sets of each chromosome, which is known as triploidy.
- A trisomy occurs when there is an extra copy of any one chromosome — 3 copies instead of 2.
- A monosomy occurs when there is a missing copy of any one chromosome — 1 copy instead of 2.
- Triploidy occurs when there are 3 copies of all the chromosomes.
At present there are 2 options to ascertain the chromosome health of a fetus in pregnant women:
- Non-invasive Method. e.g. Combined test
- Invasive Method. This is a diagnostic test with 100% detection for the aneuploidies but there is a small risk of miscarriage. e.g. CVS and amniocentesis.
The NIPT test will help women decide if they want a CVS or amniocentesis to confirm chromosomal abnormalities after a positive screen result or abnormal scan findings. Amniocentesis and CVS are invasive tests and carry a small risk of miscarriage.
Most women who have the NIPT test will probably find out their baby is at low risk for the conditions tested. This means that the chance of the baby having one of these conditions is very low, which can be reassuring. When the test result shows a high risk, it is important to talk with your doctor about your next steps.
Why NIPT?
At present this is the best method for screening for Down syndrome.
Maternal blood contains circulating cell-free DNA fragments originating from both the mother and the placenta. The proportion fetal DNA derived from the placenta with respect to total amount of cfDNA is known as the fetal fraction.
Fetal fraction of DNA in the mother’s blood can vary greatly throughout gestation; it does tend to be lower earlier in the pregnancy. The lower the fetal fraction, less sensitive is the test. For e.g. if the fetal fraction is only 4% than the test performs at 60% sensitivity whereas if the fetal fraction is more than 8% it performs at greater than 99% sensitivity.